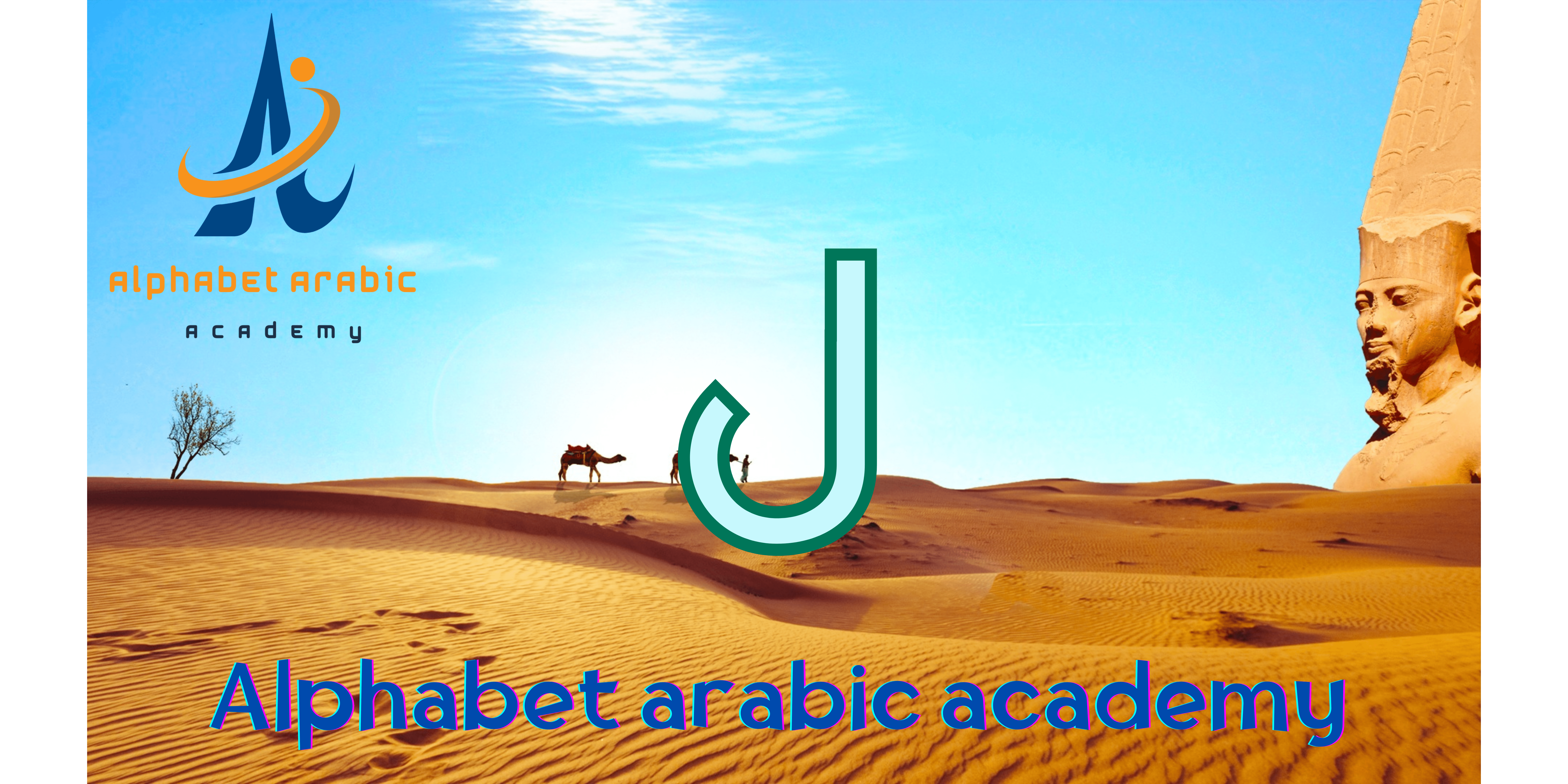
lam arabic The Arabic alphabet is the foundation of the Arabic language, consisting of 28 letters, each with its unique shape and sound. These letters form the basis of written and spoken Arabic, making it essential to understand their individual characteristics and functions. Among these letters, the letter Lam (ل) holds significant importance. Recognized for its distinctive cursive appearance, the letter Lam is pronounced as /l/, similar to the ‘L’ sound in English.

Positioned as the 23rd letter in the Arabic alphabet, Lam is a versatile character that can appear at the beginning, middle, or end of a word, altering its form accordingly. Its connectivity allows it to seamlessly link with preceding and following letters, contributing to the fluidity of Arabic script. Mastering the letter Lam is crucial for learners aiming to achieve proficiency in reading and writing Arabic.
This guide aims to facilitate your understanding of the letter Lam by providing various word samples, showcasing its usage in different contexts. By dissecting these examples, you will gain insights into the practical applications of Lam and enhance your overall command of the Arabic language. Embark on this learning journey to explore the nuances of the letter Lam and its integral role in Arabic linguistics.
The shapes of the letter Lam ل:
| TERMINAL | MIDDLE | INITIAL | ISOLATED |
|---|---|---|---|
| ـل | ـلـ | لـ | ل |
Pronunciation of Lam
The Arabic letter Lam (ل) is pronounced as /l/ in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). This sound is a voiced alveolar lateral approximant, which means that the sound is produced by allowing the airstream to flow along the sides of the tongue, with the tongue touching the alveolar ridge just behind the upper front teeth. This sound is found in many languages, making it relatively easy for learners to grasp.
In English, the sound of Lam is similar to the “l” in words such as “lamp,” “love,” and “life.” However, it is important to note that in Arabic, the pronunciation of Lam remains consistent without the variation that can occur in English, such as the “dark l” found in words like “all” or “ball.” In Arabic, whether Lam appears at the beginning, middle, or end of a word, its pronunciation does not change.
Consider the following examples to understand the consistency of Lam’s pronunciation in Arabic:
- At the beginning: لحم (lahm) meaning “meat”
- In the middle: صالح (salih) meaning “righteous”
- At the end: جمل (jamal) meaning “camel”
One helpful tip for learners is to practice the pronunciation of Lam in isolation and within words. This practice can reinforce the sound and its placement in different contexts. Additionally, listening to native speakers pronounce Lam in various words can provide an auditory benchmark that aids in developing accurate pronunciation.
When learning the Arabic alphabet, mastering the writing of each letter is crucial. The letter Lam (ل) is an essential component of the Arabic script, and understanding its various forms will significantly enhance your writing skills. Like other Arabic letters, Lam changes its shape depending on its position within a word. These positions include isolated, initial, medial, and final forms.
Isolated Form
The isolated form of Lam is written independently of other letters. To write Lam in this form, start with a short vertical stroke from top to bottom, followed by a smooth, curved stroke extending to the left. This shape is simple and serves as the foundation for the other forms.
Initial Form
When Lam appears at the beginning of a word, it is written differently. Begin with a short horizontal stroke from right to left. Then, continue with a smooth curve that extends downward, similar to a hook. This form connects seamlessly to the next letter, emphasizing the fluidity of Arabic script.
Medial Form
The medial form of Lam appears in the middle of a word, connecting to both the preceding and following letters. Start with a short horizontal stroke from right to left, followed by a small vertical stroke downwards. Then, continue the stroke downwards, curving it to the left. This form ensures a smooth transition between letters, maintaining the script’s elegance.
Final Form
The final form of Lam appears at the end of a word. It begins similarly to the medial form, with a short horizontal stroke from right to left and a vertical stroke downwards. However, the final form extends further down and curves more pronouncedly to the left, completing the word gracefully.
To aid in practice, visual aids such as diagrams and stroke order animations can be invaluable. These tools provide a step-by-step guide to writing Lam correctly, helping learners visualize and replicate the letter’s forms accurately. By regularly practicing these steps, learners can achieve proficiency in writing the letter Lam, contributing to their overall Arabic script mastery.
Common Words with Lam
The Arabic letter Lam (ل) appears frequently in Arabic vocabulary, making it an essential letter to master for anyone learning the language. Below are several common Arabic words that contain the letter Lam, along with their English translations, pronunciation guides, and example sentences to illustrate their usage in everyday conversations.
1. سلام (Salam) – Peace
Pronunciation: /sa-laam/
Example Sentence: سلام عليكم (Salam Alaikum) – Peace be upon you.
2. كلمة (Kalima) – Word
Pronunciation: /ka-li-mah/
Example Sentence: هذه كلمة جميلة (Hadhihi Kalima Jameela) – This is a beautiful word.
3. قلم (Qalam) – Pen
Pronunciation: /qa-lam/
Example Sentence: أحتاج إلى قلم (Ahtaaj ila Qalam) – I need a pen.
4. طاولة (Taawila) – Table
Pronunciation: /taa-wi-la/
Example Sentence: الكتاب على الطاولة (Al-Kitab Ala Taawila) – The book is on the table.
5. ولد (Walad) – Boy
Pronunciation: /wa-lad/
Example Sentence: الولد يلعب في الحديقة (Al-Walad Yal’ab fi Al-Hadika) – The boy is playing in the garden.
6. ليل (Layl) – Night
Pronunciation: /layl/
Example Sentence: الليل هادئ (Al-Layl Hadi’) – The night is quiet.
These examples demonstrate how the letter Lam is used in various contexts, enriching the learner’s vocabulary and enhancing their understanding of its practical applications. By regularly practicing these words in sentences, learners can strengthen their grasp of the Arabic language and its nuances.
The letter Lam ل with the Harakat حركات:
The letter Lam ل with fat.ha فتحة:
| Arabic | English | Transliteration |
|---|---|---|
| قَلَم | Pen | Qalam |
| لَون | Color | Lawn |
| عَلَم | Science | A’lam |
The letter Lam ل with the Damma ضمة:
| Arabic | English | Transliteration |
|---|---|---|
| لُعبة | Game/Toy | Luo’uba |
| لُؤلؤ | Pearl | Lu’lu’ |
| لُحوم | Meats | Luhum |
The letter Lam ل with Kasra كسرة:
| Arabic | English | Transliteration |
|---|---|---|
| لِسان | Tongue | Lisan |
| لِص | Thief | Liss |
| لِباس | Clothes | Libas |
The letter Lam ل with Sukuun سكون:
| Arabic | English | Transliteration |
|---|---|---|
| ملْعقة | Spoon | Mela’aqa |
| بصلْ | Onions | Bassal |
| عِلْم | Science | I’lm |
Note: The transliteration provided here is a general approximation of the pronunciation. The actual pronunciation may vary slightly depending on the specific dialect and context. It’s always recommended to listen to native speakers or use audio resources to refine your pronunciation.
Lam in Arabic Grammar
In Arabic grammar, the letter Lam (ل) occupies a significant role in the linguistic structure and formation of words. Its versatility and prevalence make it an essential component of the Arabic language. One of the primary functions of Lam is its usage in definite articles. The definite article in Arabic is “Al-” (ال), where Lam combines with the letter Alif (ا) to form “Al-” which means “the” in English. This construction is pivotal in assigning definiteness to nouns, thereby transforming a general term into a specific one, such as “kitab” (book) to “al-kitab” (the book).
Lam also interacts with other letters and sounds to form conjunctions. For example, Lam is used in the conjunction “li-” (لِ), which translates to “for” or “to” in English. This conjunction is crucial for constructing prepositional phrases and conveying relationships between actions and objects. For instance, “li-kitabi” (لكتاب) means “for the book,” indicating the purpose or recipient of an action.
Another grammatical role of Lam is found in the structure of verbs and nouns. In verb conjugation, Lam can serve as the root letter in various verb forms, impacting the meaning and tense of the verb. For instance, the root verb “la’iba” (لعب) means “to play.” When Lam is part of a triliteral root, it can significantly influence the verb’s derivations and inflections.
Furthermore, Lam is also instrumental in the formation of possessive structures. When attached to pronouns, it helps indicate possession or association. For example, “li-” followed by a pronoun, such as “li” + “hu” (لِهُ), forms “lahu” (لَهُ), meaning “for him” or “his.”
Overall, Lam’s interaction with other letters and sounds in Arabic grammar is multifaceted. Its presence in definite articles, conjunctions, verb roots, and possessive structures underscores its indispensable role in the linguistic and syntactical framework of the Arabic language.
Cultural Significance of Lam
The Arabic letter Lam (ل) holds substantial cultural and historical significance within Arabic-speaking communities. As a consonant in the Arabic alphabet, Lam is not just a phonetic element, but also a symbol interwoven with various aspects of Arab culture and heritage. One of the most prominent manifestations of Lam is in the famous Arabic name “Laila,” which means night. This name is deeply rooted in Arabic poetry and literature, often symbolizing beauty and mystery.
Moreover, Lam features prominently in the names of several historical and contemporary figures. Consider the name “Ali,” which is associated with numerous influential personalities, including Ali ibn Abi Talib, the cousin and son-in-law of the Prophet Muhammad. The letter Lam in “Ali” is an example of how this letter contributes to names that carry significant cultural and historical weight.
Additionally, Lam finds its place in the names of important locations. For instance, “Lebanon” (Lubnān in Arabic) begins with the letter Lam. Lebanon is renowned for its rich history, cultural diversity, and contributions to arts and literature. The presence of Lam in the name of such a significant country underscores its importance in geographical nomenclature within the Arabic-speaking world.
In the realm of phrases and idioms, Lam appears in expressions that convey wisdom and cultural values. The phrase “Laka Allah” (لك الله), which translates to “May God be with you,” is an example of how Lam is integrated into everyday language to express goodwill and blessings. This phrase exemplifies the deep spiritual and cultural resonance that the letter Lam holds in Arabic communication.
Through its incorporation in names, places, and phrases, the letter Lam serves as a bridge connecting language with cultural identity. Understanding its cultural significance enriches the linguistic journey of learning the Arabic alphabet, providing learners with a deeper appreciation of the language and its cultural contexts.
Interactive Exercises and Practice
To reinforce your understanding of the Arabic letter Lam, we have designed a series of interactive exercises and practice activities. These activities aim to enhance both your recognition and production skills, ensuring a comprehensive grasp of the letter. Below are some of the tailored exercises that you can engage in:
Fill-in-the-Blank Exercises
In these exercises, you’ll be given sentences with missing letters where you need to correctly identify and place the letter Lam. This will help you become more familiar with its appearance in different word contexts. For instance:
1. ___م (Insert the letter Lam to complete the word “علم” meaning “knowledge”)
2. كـ___ (Insert the letter Lam to complete the word “كلب” meaning “dog”)
3. ___ن (Insert the letter Lam to complete the word “ليل” meaning “night”)
Matching Games
Matching games are an excellent way to visually associate the letter Lam with its corresponding words. You’ll be presented with a list of words and a list of meanings, and your task is to match them correctly. For example:
1. ليمون – Lemon
2. لعب – Played
3. لسان – Tongue
Online Quizzes
Engage in online quizzes that test your knowledge of the letter Lam. These quizzes are designed to be both challenging and educational, featuring multiple-choice questions, true or false statements, and short-answer questions. Sample quiz questions might include:
1. What is the correct pronunciation of the letter Lam?
2. Identify the letter Lam in the following word: “سلام” (meaning “peace”)
3. True or False: The letter Lam can only appear at the beginning of a word.
By incorporating these interactive exercises into your study routine, you’ll solidify your understanding and usage of the Arabic letter Lam. These activities are not only educational but also engaging, making the learning process enjoyable and effective.
Conclusion and Further Learning Resources
Throughout this blog post, we have explored the Arabic letter Lam in depth. We began by understanding its pronunciation and unique characteristics. We then delved into its various forms and how it is written in different positions within a word. Additionally, we highlighted common words that feature the letter Lam, providing you with practical examples to enhance your learning experience.
Mastering the Arabic letter Lam is a significant step in your journey to learning the Arabic language. Regular practice and consistent exposure to the letter in diverse contexts will undoubtedly reinforce your understanding. To further aid your learning, numerous resources are available that can complement your studies.
For a structured approach, consider enrolling in online courses such as those offered by platforms like Coursera or Udemy, which provide comprehensive lessons on the Arabic alphabet and language. Additionally, language learning apps such as Duolingo and Rosetta Stone offer interactive exercises and quizzes that can help reinforce your knowledge of the Arabic letter Lam and other letters.
Books are also an invaluable resource for deepening your understanding. Titles like “Easy Arabic Alphabet” by Jane Wightwick and Mahmoud Gaafar or “Mastering Arabic Script” by Jane Wightwick and Mahmoud Gaafar provide detailed explanations and practice exercises specifically focused on Arabic script and letters.
Engaging with native Arabic speakers through language exchange programs or using platforms like iTalki can provide practical experience and enhance your pronunciation and comprehension. Additionally, watching Arabic language videos or listening to Arabic music and podcasts can offer a more immersive learning experience.
By utilizing these resources, you can continue to build upon the foundation you have established in this blog post. The journey to mastering Arabic is a rewarding one, and with dedication and the right tools, you will achieve fluency and a deeper appreciation of this rich and beautiful language.
Are you ready to increase your Arabic skills? Explore our engaging Arabic Lessons for Beginners starting at just $40. Visit our website at Alphabet Arabic Academy for more comprehensive resources. For personalized guidance, please fill our booking form on the Contact Us form.
For detailed pricing options, check out:
Stay connected with us on social media for the latest updates, tips, and interactive content. Embrace the beauty of every letter, discover the hidden in every stroke, and let your journey in Arabic begin today!
Happy learning!